Last Updated on October 9, 2023
Leben in Deutschland test (Orientierungstest, Einburgerungstest) has several questions about the relationship between Germany and other countries (mostly Europe). There are also a few questions about migrants, but more from a historical perspective.
Note: This post does not include the changes that will occur with the UK’s exit from the EU.
All posts about #Leben in Deutschland test
Part 1, Part 2, Part 3-1, Part 3-2, Part 4, Part 5-1, Part 5-2
Part 6, Part 7, Part 8, Part 9, Part 10
About Deutschtest für Zuwanderer
Who can apply for German citizenship
Germany is a member of various international associations and organizations
1. Since 1954 (Paris Agreements) Germany has been a NATO member.
2. In 1957, the Treaty of Rome was signed. France, Germany, Italy, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg established the European Economic Community (EEC, Europäische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft – EWG). The objectives of the agreement were the creation of a customs union, a unified agricultural policy, free movement of capital, labor and services between the member states of the EEC. The EEC existed until 1993. During this time, Great Britain, Denmark, Ireland, Greece, Spain, Portugal joined it.
3. In 1985, an agreement was signed on the gradual abandonment of border control by representatives of Belgium, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, France and the FRG on the Princess Marie-Astrid ship in the middle of the Moselle, at the convergence of the borders of Luxembourg, France and Germany. The agreement was named after the nearest village of Schengen to this place (Schengener Abkommen).
The visa-free regime is fully applied in the territory of 22 EU countries. Some countries use it limitedly, and some do not use it at all. In addition, the visa-free regime is applied by countries belonging to the European Economic Area and not belonging to the EU (Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland).
4. In 17 EU countries, including Germany, a single European currency, the euro, has been introduced. In non-cash payments, the euro was introduced from January 1, 1999, in cash – from January 1, 2002.
European Union
5. In 1993, on the basis of the EEC, the European Union (Europäische Union, EU) was created, the institutions of the Community became the institutions of the Union.
The European Union before 2021 included 28 states. All these countries have a common system of laws that creates a common market that guarantees the free movement of people, goods, capital and services. The Union passes laws (directives, statutes and regulations), as well as develops general policies in the field of trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development.
The most important EU institutions are the European Commission, the Council of the European Union, the European Council, the Court of Justice of the European Union, the European Court of Auditors and the European Central Bank.
EU institutions
European Council is the highest political body of the EU, consisting of the heads of state and government of the member states and their deputy foreign ministers. The Council determines the main strategic directions for the development of the EU.
European Commission is the highest executive body of the European Union. Consists of 28 27 members, one from each member state. When exercising their powers, they are independent, act only in the interests of the EU, and have no right to engage in any other activity. Member states have no right to influence the members of the European Commission. European Commission is formed every 5 years. The Commission comes up with legislative initiatives, and after approval, controls their implementation. The headquarters is in Brussels.
European Parliament is directly elected every five years by EU citizens. Members of the European Parliament do not unite according to their citizenship, but according to their political orientation.
The main role of the European Parliament is legislative activity. In addition, almost any decision of the EU Council requires either the approval of Parliament, or at least a request for its opinion. Parliament controls the work of the Commission and has the right to dissolve it. The European Parliament meets in Strasbourg or Brussels.
Council of the European Union, one of the Union’s two legislative bodies and one of its seven institutions. The Council consists of 27 ministers of the governments of the member states. Who participates depends on the issues in question. Moreover, despite the different participants, the Council is considered a single body. In addition to legislative powers, the Council also has some executive functions in the area of foreign policy and security policy.
The Court of Justice of the European Union meets in Luxembourg and is the EU’s highest court.
Situation with migrants
After the war, the FRG and the GDR had a great need for workers. Therefore, agreements were concluded allowing the recruitment of labor migrants in other countries (Gastarbeiter).
The first country with which such an agreement was concluded was Italy (1955), then Greece (1960). Turkey really wanted to conclude an agreement, but part of the FRG leadership resisted, but under pressure from the United States was forced to give up. Later, treaties were also concluded with Morocco, Portugal, Tunisia and Yugoslavia. It was assumed that the workers would work for a year or two, then return to their homeland with new knowledge that would help the development of production in these countries. In practice, migrants did not want to return home, where there was no work for them.
In the GDR there were also guest workers from countries oriented towards the USSR: mainly Vietnam, Cuba, Mozambique, Angola. Migrants lived according to strict rules and worked under discriminatory conditions. The migrant workers lived in special settlements, and integration with the Germans was not only not supported, but not even assumed.
Follow me
Questions
173. Die Bundesrepublik Deutschland ist ein Gründungsmitglied …
– des Nordatlantikpakts (NATO).
– der Vereinten Nationen (VN).
– der Europäischen Union (EU).
– des Warschauer Pakts.
The Federal Republic of Germany is one of the founders … (3)
221. Deutschland ist Mitglied des Schengener Abkommens. Was bedeutet das?
– Deutsche können in viele Länder Europas ohne Passkontrolle reisen. (Germans can travel to many European countries without passport control)
– Alle Menschen können ohne Personenkontrolle in Deutschland einreisen. (All people can enter Germany without an identity check)
– Deutsche können ohne Passkontrolle in jedes Land reisen. (Germans can travel to any country without passport control)
– Deutsche können in jedem Land mit dem Euro bezahlen. (Germans can pay with the euro in any country)
Germany is a member of the Schengen Agreement. What does this mean? (1)
222. Welches Land ist ein Nachbarland von Deutschland?
– Ungarn
– Portugal
– Spanien
– Schweiz
Which country borders on Germany? (4)
223. Welches Land ist ein Nachbarland von Deutschland?
– Rumänien
– Bulgarien
– Polen
– Griechenland
Which country borders on Germany? ((3)
224. Was bedeutet die Abkürzung EU?
– Europäische Unternehmen
– Europäische Union
– Einheitliche Union
– Euro Union
What does the abbreviation EU stand for? (2)
225. In welchem anderen Land gibt es eine große deutschsprachige Bevölkerung?
– Tschechien
– Norwegen
– Spanien
– Österreich
In which other country does the majority of the German-speaking population live? (4)
226. Welche ist die Flagge der Europäischen Union?
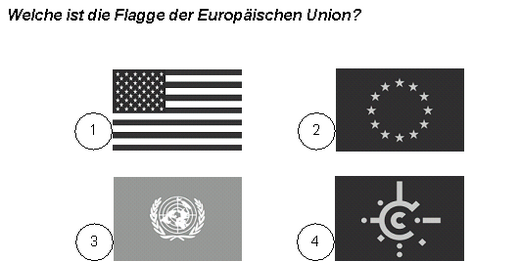
– 1
– 2
– 3
– 4
What is the flag of the European Union? (2)
227. Welches Land ist ein Nachbarland von Deutschland?
– Finnland
– Dänemark
– Norwegen
– Schweden
Which country borders on Germany? (2)
229. Welches Land ist ein Nachbarland von Deutschland?
– Spanien
– Bulgarien
– Norwegen
– Luxemburg
Which country borders on Germany?(4)
230. Das Europäische Parlament wird regelmäßig gewählt, nämlich alle …
– 5 Jahre.
– 6 Jahre.
– 7 Jahre.
– 8 Jahre.
The European Parliament is periodically elected, every … (1)
231. Was bedeutet der Begriff „europäische Integration“?
– Damit sind amerikanische Einwanderer in Europa gemeint.
(This means American immigrants in Europe.)
– Der Begriff meint den Einwanderungsstopp nach Europa.
(The term means the immigration stop to Europe)
– Damit sind europäische Auswanderer in den USA gemeint.
(This means European emigrants in the USA.)
– Der Begriff meint den Zusammenschluss europäischer Staaten zur EU.
(The term means the union of European states to form the EU.)
What does the concept of “European integration” mean? (4)
232. Wer wird bei der Europawahl gewählt?
– die Europäische Kommission
– die Länder, die in die EU eintreten dürfen
– die Abgeordneten des Europäischen Parlaments
– die europäische Verfassung
Who is elected during the European elections? (3)
233. Welches Land ist ein Nachbarland von Deutschland?
– Tschechien
– Bulgarien
– Griechenland
– Portugal
Which country borders on Germany? (1)
234. Wo ist der Sitz des Europäischen Parlaments?
– London
– Paris
– Berlin
– Straßburg
Where does the European Parliament sit? (4)
235. Der französische Staatspräsident Francois Mitterrand und der deutsche Bundeskanzler Helmut Kohl gedenken in Verdun gemeinsam der Toten beider Weltkriege. Welches Ziel der Europäischen Union wird bei diesem Treffen deutlich?
– Freundschaft zwischen England und Deutschland (Friendship between England and Germany)
– Reisefreiheit in alle Länder der EU (Freedom to travel to all EU countries)
– Frieden und Sicherheit in den Ländern der EU (Peace and security in the countries of the EU)
– einheitliche Feiertage in den Ländern der EU (uniform holidays in the countries of the EU)
French President François Mitterrand and German Chancellor Helmut Kohl paid tribute to those killed in two world wars in Verdun. What was the purpose of the European Union in this case? (3)
236. Wie viele Mitgliedstaaten hat die EU heute?
– 21
– 23
– 25
– 28
How many countries are currently in the EU? (4) This answer will be certainly changed to 27 in 2021.
237. 2007 wurde das 50-jährige Jubiläum der „Römischen Verträge“ gefeiert. Was war der Inhalt der Verträge?
– Beitritt Deutschlands zur NATO (Germany joins NATO)
– Gründung der Europäischen Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft (EWG) (Foundation of the European Economic Community EEC)
– Verpflichtung Deutschlands zu Reparationsleistungen (Germany’s obligation to pay reparations)
– Festlegung der Oder-Neiße-Linie als Ostgrenze (Establishment of the Oder-Neisse line as the eastern border)
2007 marked the 50th anniversary of the Treaty of Rome. What is the content of the contract? (2)
238. An welchen Orten arbeitet das Europäische Parlament?
– Paris, London und Den Haag
– Straßburg, Luxemburg und Brüssel
– Rom, Bern und Wien
– Bonn, Zürich und Mailand
In which cities does the European Parliament work? (2)
239. Durch welche Verträge schloss sich die Bundesrepublik Deutschland mit anderen Staaten zur Europäischen Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft zusammen?
– durch die „Hamburger Verträge“
– durch die „Römischen Verträge“
– durch die „Pariser Verträge“
– durch die „Londoner Verträge“
By what treaty did Germany and other states form the European Economic Community? (2)
240. Seit wann bezahlt man in Deutschland mit dem Euro in bar?
– 1995
– 1998
– 2002
– 2005
Since what year did the euro come into circulation in cash? (3)
297. Aus welchem Land sind die meisten Migranten / Migrantinnen nach Deutschland gekommen?
– Italien
– Polen
– Marokko
– Türkei
From which country did the majority of migrants come to Germany? (4)
298. In der DDR lebten vor allem Migranten aus …
– Vietnam, Polen, Mosambik.
– Frankreich, Rumänien, Somalia.
– Chile, Ungarn, Simbabwe.
– Nordkorea, Mexiko, Ägypten.
In the GDR lived mainly migrants from … (1)
299. Ausländische Arbeitnehmer und Arbeitnehmerinnen, die in den 50er und 60er Jahren von der Bundesrepublik Deutschland angeworben wurden, nannte man …
– Schwarzarbeiter / Schwarzarbeiterinnen
– Gastarbeiter / Gastarbeiterinnen
– Zeitarbeiter / Zeitarbeiterinnen
– Schichtarbeiter / Schichtarbeiterinnen
Foreign workers who arrived in Germany in the 60s were called … (2)
300. Aus welchem Land kamen die ersten Gastarbeiter / Gastarbeiterinnen nach Deutschland?
– Italien
– Spanien
– Portugal
– Türkei
What country did the first guest workers come from?(1)
Other posts about Orientierungstest (Test Leben in Deutschland) – #orientierungstest
Do you enjoy the site without cookies and maybe without ads? This means that I work for you at my own expense.
Perhaps you would like to support my work here.
Or Cookie settings change: round sign bottom left
